| Product Name | Hypotube |
|---|---|
Application | Endoscopic instruments, catheter shafts, robotic surgical systems |
Direction | Two, four, 360 degree |
Materials | Stainless Steel 304, 316, Ni-Ti, Cobalt Chrome |
Hardness | HRC 22-25 (304), HRC 38-46 (17-7PH), HRC 40-50 (MP35N) |
Diameter | 0.3mm to 20mm |
Material Length | Up to 3m |
Part Length | 0.2mm to 3mm |
Kerf Width | 15um to 30um |
Tolerance | +/-0.01mm |
Manufacturing | Laser Cutting |
Certification | ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485 |
Facilities | 5-Axis Laser Cutting Machine |
Packing | PP bag or tailor-made packing on request |
What is Laser Cut Hypotube?
Laser cut hypotube is a small-diameter, thin-walled metal tube manufactured with advanced laser cutting technology. These flexible tubes are vital in various medical procedures, especially in catheter assemblies and interventional devices like flexible catheter shafts and delivery systems. Their small size and flexibility enable navigation through complex anatomical structures, such as blood vessels. Additionally, the hollow design allows for the control of medical tools and the delivery of therapeutic drugs during procedures.
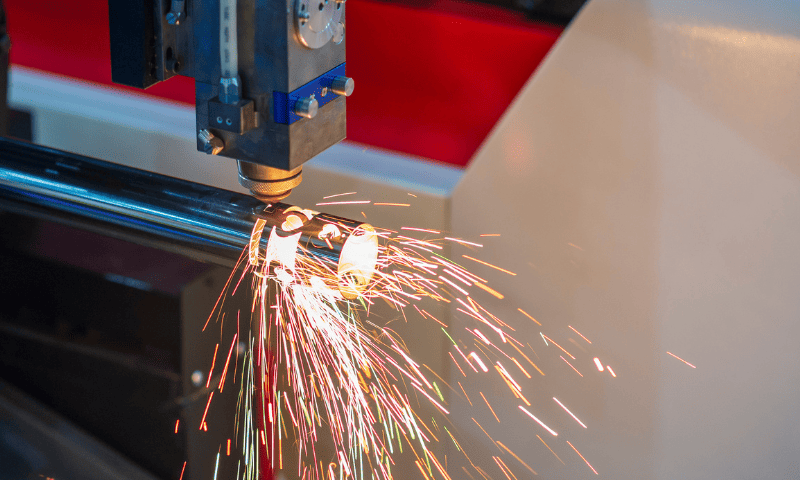

Among these steps, laser cutting is a crucial process in the production of hypotubes, enabling the creation of complex designs with exceptional precision essential for medical applications. This advanced non-contact technique allows for the formation of detailed features and micron-sized shapes without causing mechanical deformation, effectively eliminating the risk of burrs or defects.
Manners utilizes cutting-edge five-axis laser cutting machines capable of achieving sub-micron repeatability, enabling engineers to custom-design hypotube-catheter systems that navigate complex anatomical pathways. The versatility of laser cutting supports various designs, including straight cuts, slots, angled cuts, and intricate patterns, making it easy to tailor hypotubes for specific applications. Additionally, this process can be configured for both manual and automated processing, enhancing manufacturing efficiency.

Solutions
Our Laser Cut Hypotube Solutions cater to modern medical and industrial applications by utilizing advanced five-axis laser cutting technology. This process allows us to produce high-precision hypotubes essential for procedures like catheter assemblies, enabling intricate designs and precise dimensions for optimal performance in complex anatomical pathways.
We provide customization based on material selection and customer specifications, using 304 and 316 stainless steel, 17-7PH, MP35N, and Nitinol. For nitinol hypotube, we carefully control the temperature during processing to preserve its unique properties. Additionally, we offer a PTFE coating for enhanced lubricity and improved traceability.

Focusing on quality and efficiency, our solutions minimize defects such as burrs and mechanical deformation, maintaining the integrity of each hypotube. Whether you need small prototypes or large production runs, our Laser Cut Hypotube Solutions provide the reliability and customization you require.
What Are Hypotube Used For?
Hypotubes serve a wide range of purposes in both the medical field and various industrial applications.
Medical Applications
Catheters and Guide Wires: Hypotubes are extensively used in interventional devices like catheters and guide wires, where their small size and flexibility allow them to navigate complex vascular systems. This enables the precise delivery of surgical tools, devices, or drugs to specific areas in the body.
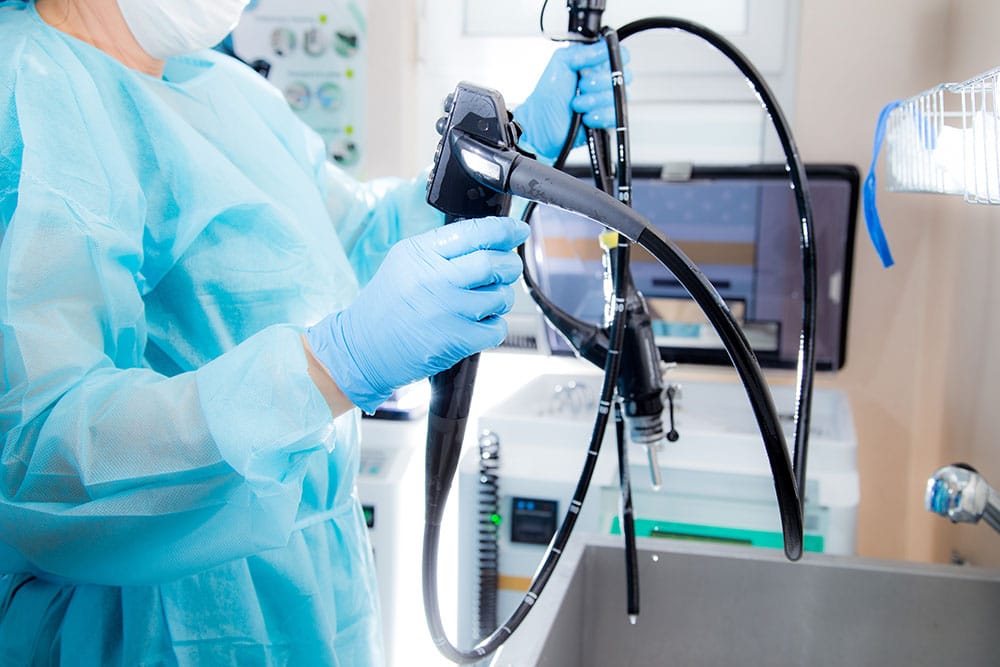
Endoscopes: In endoscopic procedures, hypotubes are utilized in the bending sections, ensuring smooth and precise navigation through delicate parts of the body.
Surgical Robots and Medical Cables: Hypotubes act as load-bearing elements and are often swaged to stainless steel or tungsten cables in surgical robots. These tubes help improve the flexibility and strength of cables used in robotic surgery and other medical instrumentation.
Needles and Cannulas: Hypotubes are used in the manufacturing of needles and cannulas, offering the precision required for minimally invasive procedures.
Heart Stents: Hypotubes are used in medical-grade stents, particularly for cardiovascular interventions, offering precision and flexibility to support blood vessel structures.
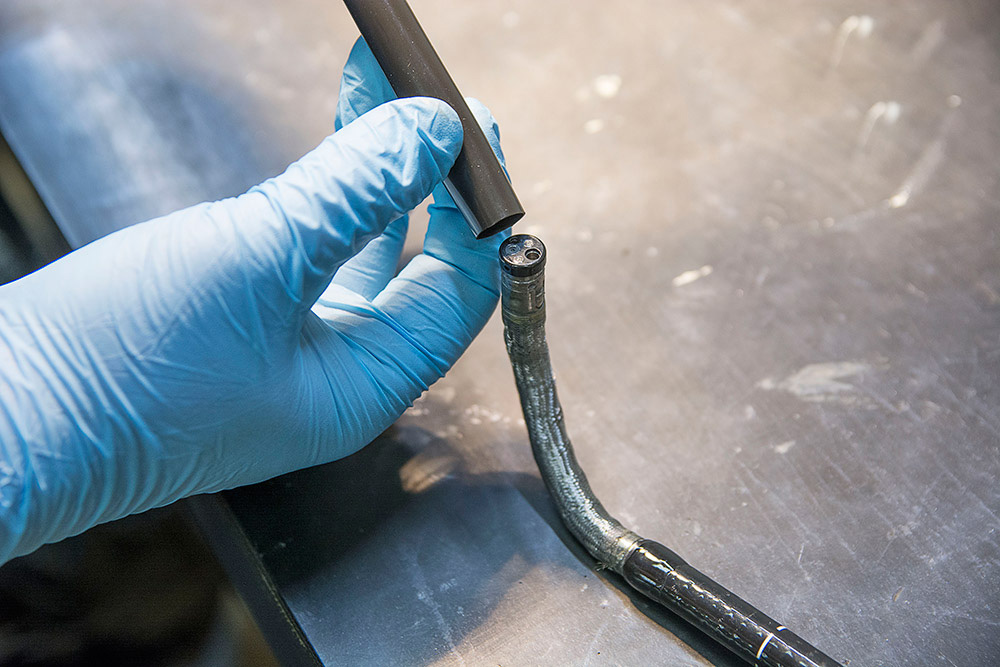

Industrial Applications
Fluid Delivery and Sensing: In industries requiring precision, such as fluid delivery systems and instrumentation, hypotubes play a key role by offering tight control and accuracy in confined spaces.
Mechanical Cable Assembly: Originally designed for use in guidewires and needles, hypotubes have become a popular alternative to traditional mechanical cables, joining cable segments or providing a load-bearing point, particularly in the robotics and precision instrumentation sectors.
Sizes and Specifications
Laser cut hypotubes come in a range of sizes and specifications to meet varying medical needs. Hypotube gauge charts help manufacturers select the right dimensions for specific applications. Manners Technology offers hypotube sizes from 0.3mm to 20mm in diameter, with wall thickness ranging from 0.06mm to 2mm.
Outer Diameters for Various Applications
| Application | Outer Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|
| Laryngoscope | 4 |
| Bronchoscope | 5 |
| Gastroscope | 6 - 10 |
| Ureterorenoscope | 3.5 |
| Arthroscope | 5 |
| Percutaneous Nephroscope | 3.5 |
| Biliary Endoscope | 4.5 |
| Colonoscope | 10 - 15 |
| Cystoscope | 1.8 - 2.8 |
Medical Materials
Manners Technology specializes in manufacturing custom hypotubes to meet a variety of needs. Our hypotubes are available in a variety of materials including 304, 316, 17-7PH, MP35N, L605, and Ni-Ti (nickel titanium alloy) with hardnesses ranging from 20 to 50 HRC. Hardness varies with material and processing techniques. These materials offer biocompatibility, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Hypotube Capabilities
Hypotubes are precision machined using advanced five-axis laser technology. The thin-walled tube is meticulously cut according to a preset computer program, cutting a long, intermittent spiral into the tube wall. Hypotubes cut on a 5-axis laser cutting machine have higher precision, finer slots and better edge quality, with slot widths ranging from 15um to 30um and a tolerance of 0.01mm, efficiently meeting various requirements.
Manners uses either a medium-powered fiber laser or an ultra-fast femtosecond laser to cut hypotubes. The fiber laser is great for cutting thicker materials quickly, while the femtosecond laser is better for very thin or delicate parts.
The femtosecond laser quickly puts energy into the material, which prevents heat from spreading and keeps heat-affected areas small when the material turns to vapor. This process creates smooth edges, often making extra finishing work unnecessary, like electropolishing.
Our 5-axis laser cutting machines can be set up for both manual and automated operations and can use either type of laser or both. They can be fitted with feeder and unloader modules for full automation. The machines can load tubes as small as 0.3 mm in diameter, like thrombectomy catheters, and can also handle tubes from 1 mm to 20 mm in diameter and up to 3 m long for hands-free production.
Why Choose Manners?
Manners Technology is a top hypotube manufacturer committed to quality and cost-effectiveness. We enhance our manufacturing process with custom machine pathing, ensuring efficient production of high-quality products.
Our design engineers work closely with customers to create tailored solutions, following Design for Manufacturability (DFM) principles for repeatable, high-quality manufacturing. Our ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 certifications demonstrate our adherence to industry standards.
With quick turnaround times—7 business days for samples and 15 business days for large orders—Manners Technology is your ideal hypotube supplier, blending speed and quality seamlessly.
FAQ
1. How are hypotubes made?
Hypotubes are made using advanced laser cutting techniques, which transform rigid tubes into flexible components by creating intricate patterns on the tube walls.
2. What are hypotubes used for?
Hypotubes are used in medical devices for procedures like flexible cystoscopy, endoscopy, and catheter-based interventions. They are also used in industrial and robotic applications.
3. What is the difference between catheter shafts and hypotubes?
Catheter shafts are often built using hypotubes. The hypotube provides structural support and flexibility, allowing the catheter to navigate complex anatomical pathways.
4. What sizes do hypotubes come in?
Hypotube sizes range from 0.3mm to 20mm in diameter, with varying lengths and wall thicknesses to meet specific medical and industrial applications.