Learn everything about heart stents: their uses, types, and the procedure for placement. Understand when stents are necessary and how to choose the right one.



A heart stent, also known as a coronary stent, is a common medical device used in cardiac interventional procedures to open up blocked arteries. They are primarily made of stainless steel, nitinol (nickel-titanium alloy), or cobalt-chromium alloy.

2.1 Stable Lesions
If a coronary angiography shows that the coronary artery is narrowed by less than 80% and the patient has no significant symptoms, astent is generally not needed. Medication can be used, and regular check-ups are necessary to monitor changes in the artery's condition.
If the angiography shows that the coronary artery is narrowed by more than 80% and the patient has noticeable symptoms like chest tightness or chest pain, and tests indicate significant myocardial ischemia, a stent is recommended.
2.2 Unstable Lesions
Patients with unstable lesions are at risk of a myocardial infarction (heart attack) at any time, which can be fatal. These patients need to undergo stent surgery as soon as possible.
The choice of a stent depends on the diameter and length of the artery and the severity of the arterial lesion. There is little difference in effectiveness between domestic and imported stents. It is recommended to choose the most suitable stent based on your specific condition during treatment.
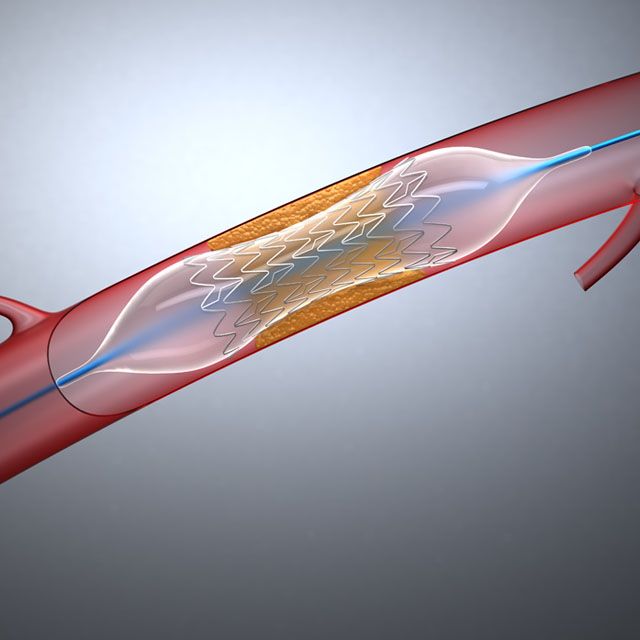
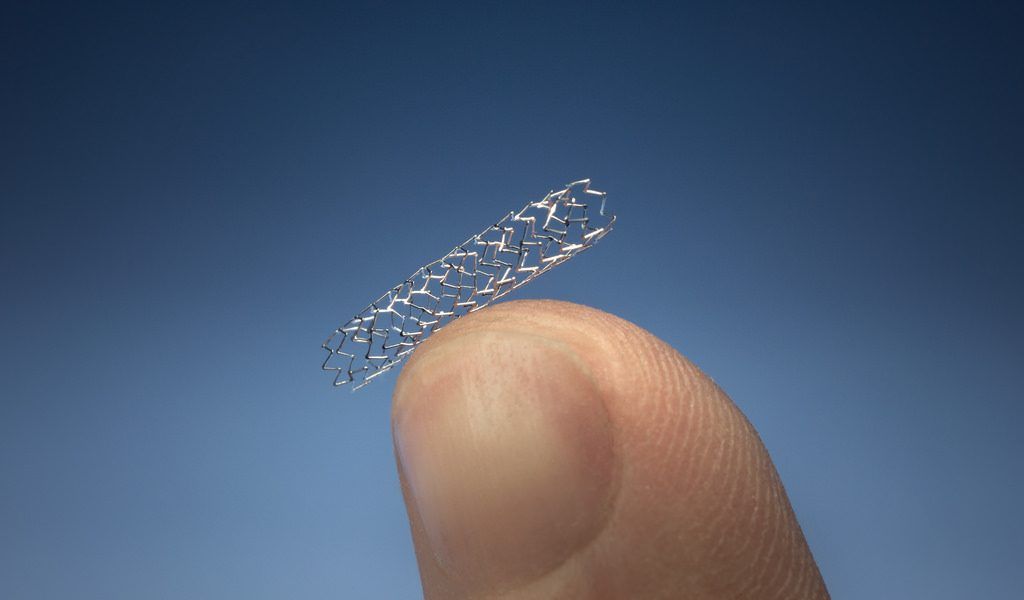
Heart stents can be made of various materials such as stainless steel, nitinol, or cobalt-chromium alloy. There are also different types of stents:
Traditional Stents: Simple metal mesh tubes.
Drug-Eluting Stents: These are coated with medication to prevent the proliferation of arterial cells and the formation of blood clots.
Covered Stents: Stents that have a membrane covering to protect the arterial wall.
Polymer Composite Stents: These stents prevent blood clots without the need for medication.
Coronary artery stent placement is a delicate procedure that takes time. If a patient needs stents in two arteries and cannot tolerate the time required for both in one session, the procedure will be split into two.
If a patient has poor kidney function, the surgery will also be done in two stages. The contrast agent used during the procedure can affect the kidneys, and doing both at once might lead to contrast-induced nephropathy.
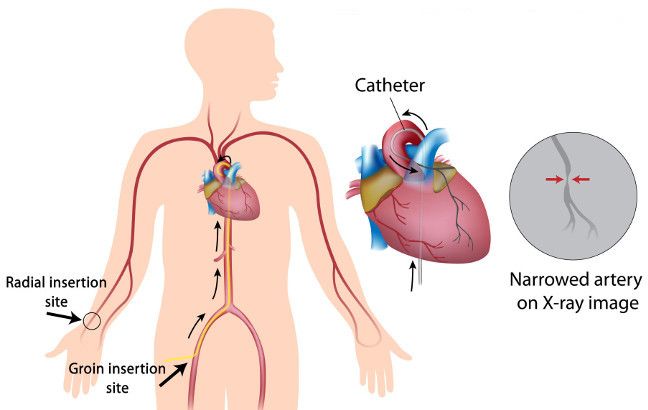
The femoral artery in the leg is larger and easier for doctors to work with, but it has a higher risk of hematoma and is harder to stop bleeding. It also requires the patient to rest in bed after the procedure.
Using the radial artery in the arm requires more skill from the doctor, but it allows the patient to resume normal activities sooner.
The following situations require a leg approach:
If the radial artery is naturally narrow or curved, making it difficult to position the catheter.
In emergencies, to save time.
For contralateral angiography, such as when placing a stent in the left coronary artery and needing to image the right coronary artery for better visualization.
Rest assured, once a stent is placed, it is embedded in the artery wall and won't come loose. In fact, avoiding exercise can lead to a decline in heart function and exercise tolerance. Patients are encouraged to engage in appropriate physical activity after surgery.
Studies show that without ongoing treatment post-surgery, the recurrence rate of the disease and mortality rate are high. So, never let your guard down! Regular follow-ups, adhering to medication, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are crucial.