Learn about left atrial catheterization, its applications in diagnosing and treating heart conditions, and the role of transseptal guiding catheters in the procedure.


The Left heart catheterization is a fundamental medical procedure within the realm of cardiology. It entails the insertion of a thin, flexible catheter into the left side of the heart, aiming to acquire diagnostic information or provide therapeutic interventions for specific cardiac conditions. Through this procedure, critical diagnostic data on the pressures and blood flow within the ventricle can be obtained, along with the collection of blood samples from the heart and the examination of heart arteries using X-ray imaging (fluoroscopy).
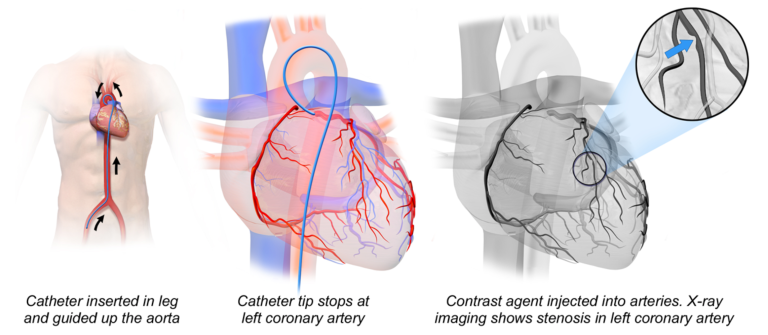
The left atrium, a pivotal chamber in the heart, is responsible for receiving oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and propelling it into the left ventricle. This action is crucial for facilitating the distribution of oxygenated blood throughout the body. Left atrial catheterization, a commonly employed medical procedure in cardiac interventions, is focused on evaluating and addressing conditions related to this crucial heart chamber.
The process of left atrial catheterization involves the careful insertion of a catheter into the left atrium using guided techniques. This catheter, made of thin and flexible medical-grade materials, is meticulously threaded through the circulatory system, reaching the left atrium under the guidance of imaging techniques. Once in position, the catheter enables the execution of diverse diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, playing a pivotal role in the comprehensive assessment and treatment of conditions associated with the left atrium. These procedures significantly contribute to enhanced cardiac health and overall well-being.
The applications of left atrial catheterization are broad and encompass both diagnostic and interventional purposes. Diagnostic uses include measuring pressures within the left atrium, assessing blood oxygen levels, and obtaining tissue samples for further analysis. Interventional applications involve procedures such as radiofrequency ablation to treat cardiac arrhythmias, closure of atrial septal defects, and placement of left atrial appendage closure devices to reduce the risk of strokes.
The catheters used in left atrial catheterization are carefully engineered to ensure flexibility, maneuverability, and biocompatibility. Modern catheters are typically designed with multiple lumens, allowing for the infusion of contrast agents, measurement of pressures, and other functionalities. They are often coated with lubricious materials to reduce friction during insertion.
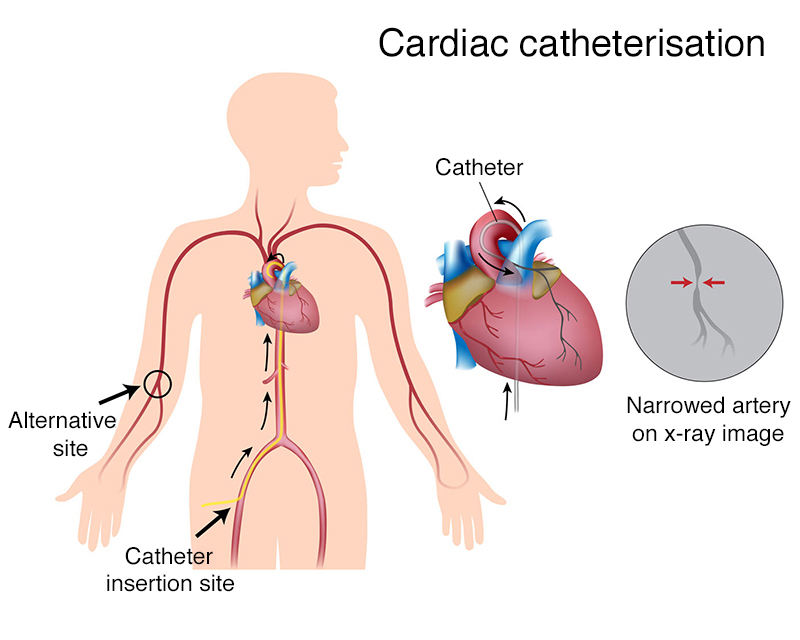
The process of left atrial catheterization involves guiding the catheter through the vascular system, often via access through the femoral vein or another appropriate entry point. Utilizing imaging techniques like fluoroscopy and echocardiography, the catheter is advanced through the veins, across the septum, and into the left atrium. Once in position, various procedures can be performed based on the specific medical requirements.
The key component being discussed below is the “transseptal guiding catheter” or called “transseptal sheath” in the left atrial catheterization.
A transseptal guiding catheter, which is also known as “transseptal sheath”, or “combination cap” (in the machining), refers to the top portion of a medical device designed in a spherical or approximately spherical shape. This design allows easier sliding over the septum wall of the heart and into the left atrium and helps reduce trauma, minimize tissue damage, and enhance the guiding capability of the device. Manners Technology produces the component transseptal guiding catheter to help the catheter, guidewire or other medical instrument can enter the left atrium, especially used in interventional procedures and endoscopic examinations.

Transseptal guiding catheters find various applications in the medical field, with one of the prominent uses being in cardiac catheterization. During cardiac catheterization, catheters designed with spherical tips aid physicians in smoothly guiding the catheter into cardiac chambers, especially in cases of complex or narrow cardiac structures. This design ensures the accuracy and success of the procedure.
Furthermore, transseptal guiding catheters are extensively used in vascular intervention procedures. In vascular interventions, the spherical design at the tip of the catheter facilitates smooth entry into the vascular system, minimizing vascular wall damage, and providing good navigational capabilities, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the procedure.
The manufacturing of transseptal guiding catheters involves several steps. Firstly, material preparation is essential, involving the selection of suitable materials that meet biocompatibility and medical device quality standards. Manufacturing transseptal guiding catheters requires the selection of appropriate materials to ensure biocompatibility, mechanical performance, and processability. Manners Technology commonly use materials including stainless steel, Ni-ti, and other medical-grade metals.
Let’s take stainless steel as an example: it possesses good mechanical strength and can withstand the external forces and pressures required by cardiac catheters, while being tough enough to ensure its bending and guiding capabilities. Its appropriate hardness ensures that the catheter can pass through blood vessels and cardiac structures without being easily deformed or broken. While being free of burs, capes, kinks, splits and twists is our most basic ability in Manners Technology.
Stainless steel is resistant to corrosion by many chemicals, ensuring stability and safety when used in living organisms. It has a dense chromium oxide layer which helps to prevent further corrosion and rust. Generally not causing allergies, allergic reactions or adverse reactions when in contact with biological tissues, stainless steel makes it one of the most commonly used materials for medical devices. Additionally, its good workability allows it to be made into complex-shaped conduits or sheaths through cutting, bending, welding and other processes.
Next, computer-aided design (CAD) software is used for the design and modeling, ensuring the tip’s shape meets the required specifications and customized designs. Subsequently, computer numerical control (CNC) machines use numerical control to execute preprogrammed machine control commands to perform various machining operations such as milling, turning, drilling, etc. In Manners, Swiss-made 7-axis longitudinal lathes and other processing equipment are utilized to cut, shape, and process the chosen materials into customized shape with seven different axes moving or controlling the cutting tools automatically, which provide flexibility and precision in machining operations. Finally, the manufactured transseptal guiding catheters come to the quality inspection to ensure dimensions, shape, and surface smoothness meet specified requirements.
Through these manufacturing steps, the quality of the transseptal guiding catheter is ensured, making it suitable for medical devices and enabling it to achieve the intended functionality and performance. Manners Technology specializes in producing medical devices, committed to providing reliable support for interventional procedures and endoscopic examinations. Continued refinement in design and manufacturing will bring more innovations and advancements to the medical field.