Explore top-performing interventional vascular devices like DKutting™ and UltraScore™. Find cutting-edge solutions for peripheral artery disease treatment. Discover innovative features and benefits for optimized patient outcomes.


Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) refers to vascular lesions other than coronary arteries and intracranial vessels, including upper limb arteries, visceral arteries, lower limb arteries, branch arteries of the aortic arch, and the aorta. Its pathological mechanism mainly involves arterial stenosis due to atherosclerosis. Globally, there are over 200 million people with varying degrees of PAD.
Common treatments for PAD include medication therapy, surgical treatment, and endovascular treatment. Endovascular treatment can be further divided into balloon angioplasty, also known as percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), stent implantation (bare metal stents and drug-eluting stents), plaque excision, drug-coated balloon (DCB), etc., with the choice of treatment modality made by the physician based on the patient's condition. Balloon angioplasty is an interventional treatment method where a balloon catheter is advanced along a guidewire track to the target lesion in the artery, and the narrowed artery is dilated using the pressure generated by balloon inflation.
The scope of application for peripheral scoring or cutting balloons typically involves the dilation of lesions within the iliac arteries, femoral arteries, iliofemoral arteries, popliteal arteries, infrapopliteal arteries, and renal arteries, as well as the treatment of obstructive lesions in autogenous or prosthetic arteriovenous fistulae.
Since 1977, balloon angioplasty (referred to as PTA) has been clinically utilized, playing a crucial role in the treatment of coronary artery vascular diseases and PAD. Balloons can be classified into three types based on design characteristics: compliant, semi-compliant, and non-compliant. Additionally, they can be further categorized into plain balloons and scoring balloons, with scoring balloons typically referring to cutting balloons (with microblades), scoring balloons (with nylon scoring elements), and dual-wire balloons (with metallic wires).
For high-resistance lesions like mild to moderate calcifications, scoring balloons can facilitate the rupture of intramural calcifications, thereby improving the dilation efficacy for calcified lesions. While plain balloons may cause tearing due to the irregular expansion of plaques, leading to intramural hematomas and increasing the risk of acute vascular occlusion, scoring balloons can guide plaque rupture to occur more frequently along the longitudinal axis of the vessel, reducing the formation of restrictive dissections. Scoring balloons are prone to adhere to the surface of plaques post-expansion, thus avoiding balloon slippage.
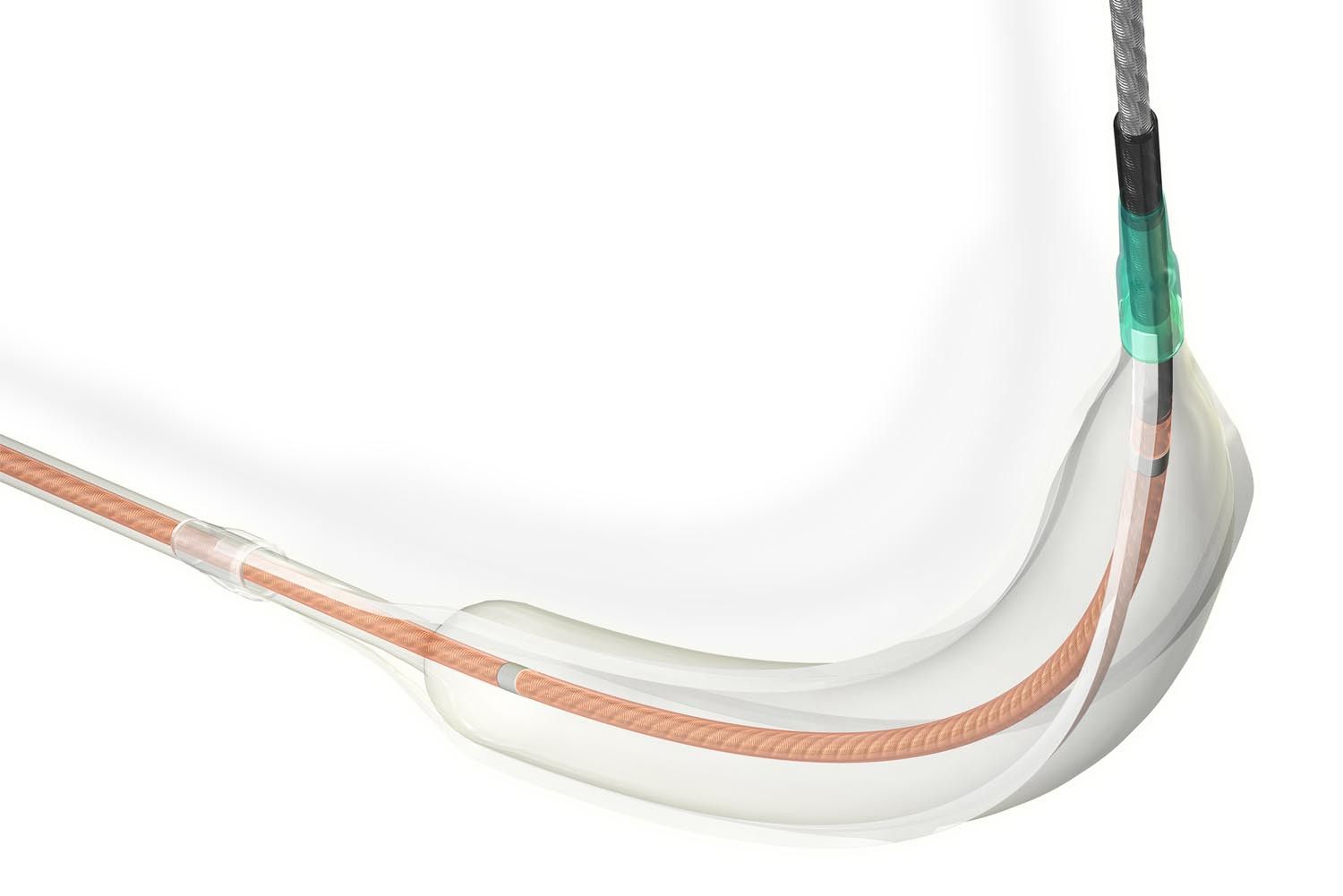
A scoring balloon involves a nitinol wire helically wrapped around the outer surface of the balloon, operating on a principle similar to dual-wire balloons, making it a type of scoring balloon.
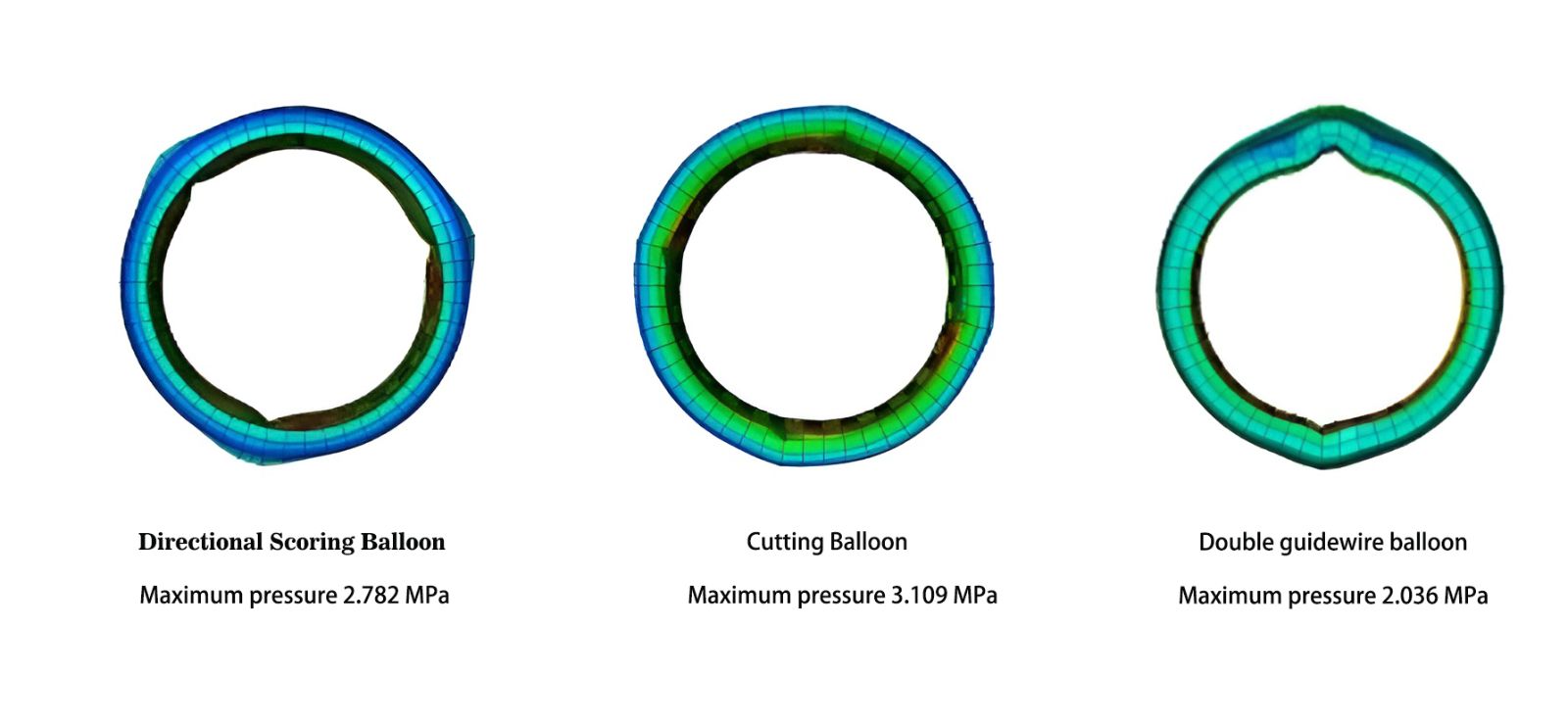
The FDA categorizes balloons with stress concentration closer to blades as cutting balloons, while those with stress distribution closer to guidewires or plain balloons are termed scoring balloons, although it does not explicitly differentiate between the stress thresholds of the two types of balloons.
Balloon angioplasty catheters achieve the reduction of vascular narrowing by expanding the distal balloon, compressing plaque within the vessel, and stretching the vessel wall. However, this procedure may also lead to complications such as intramural tears and vascular elastic recoil. For rigid narrowings, such as calcified lesions, increasing the inflation pressure of the balloon is often necessary to alleviate the severity of the narrowing and attain sufficient luminal volume.
However, the increase in inflation pressure can augment the stretching of the vessel wall, thereby increasing the likelihood of vascular injury-related complications (such as severe dissections and recoil). In cases of particularly stubborn and hard lesions, even inflating the balloon to near its burst pressure may fail to compress the plaque adequately.
Physicians have discovered that placing an additional companion guidewire outside the balloon can address this issue. When the balloon inflates, the external companion guidewire encounters the boundary of the narrowing lesion (such as calcified lesions). Due to the higher local pressure, a groove forms. As the balloon continues to expand, according to the principles of elasticity, the bottom of the groove experiences localized stress concentration, known as stress-focusing effect. This effectively crushes the hardened plaque, expanding the vessel and achieving the goal of reducing vascular narrowing. This method is referred to as the dual-wire technique.
In 1995, Sandeep et al. reported the efficacy of using a guidewire-assisted balloon angioplasty technique. In percutaneous coronary angioplasty procedures for type A or B lesions according to the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association criteria, when employing the dual-wire technique, the balloon inflation pressure was 435697.5 Pa, resulting in a final residual stenosis rate of 21%. Conversely, without using the dual-wire technique, the balloon inflation pressure was 678877.5 Pa, resulting in a final residual stenosis rate of 29%. There was a significant difference observed (P=0.001).
The design concepts of scoring balloons and dual-wire balloons stem from the dual-wire technique, which primarily integrates the guidewire with the balloon to form a cohesive unit.
Scoring balloons consist of a modification component (guidewire) and a balloon. The guidewire, made of nitinol alloy and surface-polished, is spiral-shaped and wrapped around the outer surface of the balloon, similar to the structure of nitinol stents. When the balloon is deflated, the guidewire adheres to the balloon's surface, allowing the scoring balloon to have similar navigability to a regular balloon. Once inflated, the guidewire spirals attach to the vessel wall, acting as screws to prevent the balloon from slipping.
Cutting balloons are comprised of a non-compliant balloon and longitudinally arranged microblades on the adherent surface, which cut through the plaque, creating longitudinal incisions. Due to the contact surface with the lesion made of stainless steel blades, cutting balloons exert localized forces, facilitating the cutting of hard lesions but also carrying the risk of unintended injury.
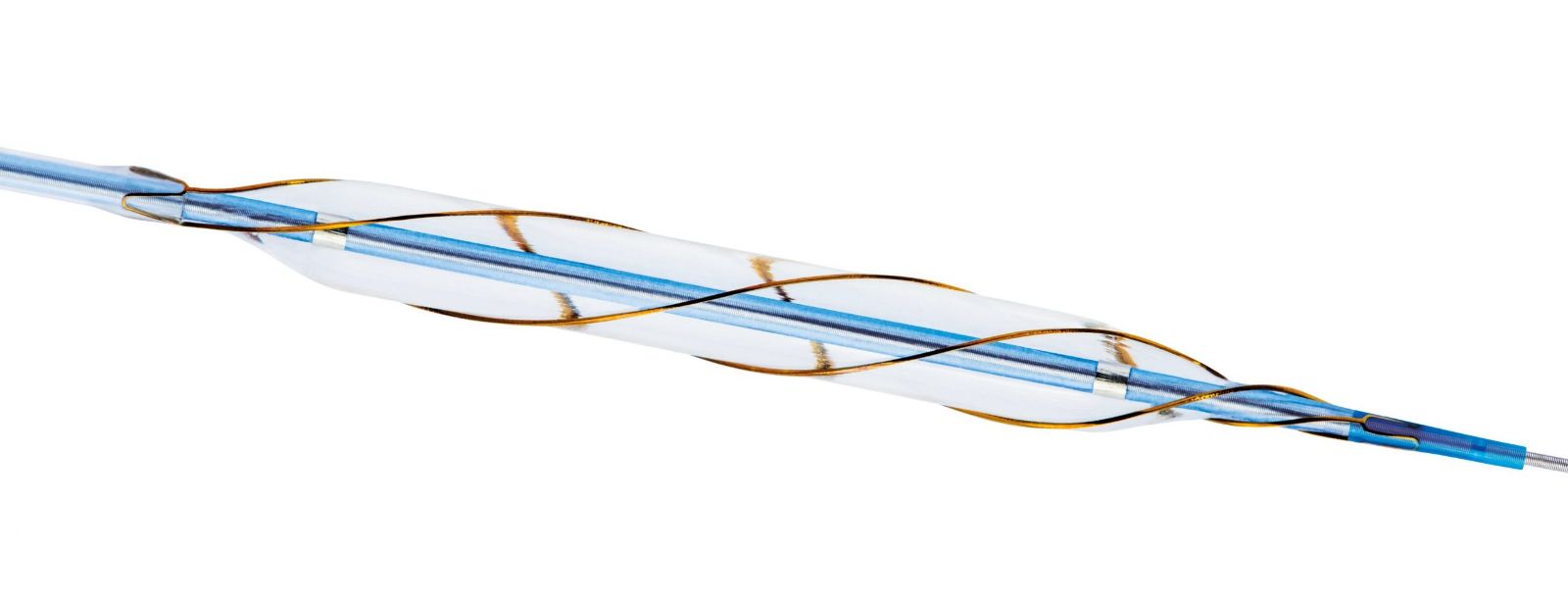
Dual-wire balloons consist of two guidewires adhered to the balloon's surface, providing a simple structure similar to placing additional guide wires beside a regular balloon. However, the guidewires may slide with the balloon, making them less secure on the vessel wall.
In contrast, cutting balloons are equipped with 3-4 sharp metal blades longitudinally mounted on the non-compliant balloon surface, allowing simultaneous cutting of the vascular lesion during balloon inflation.
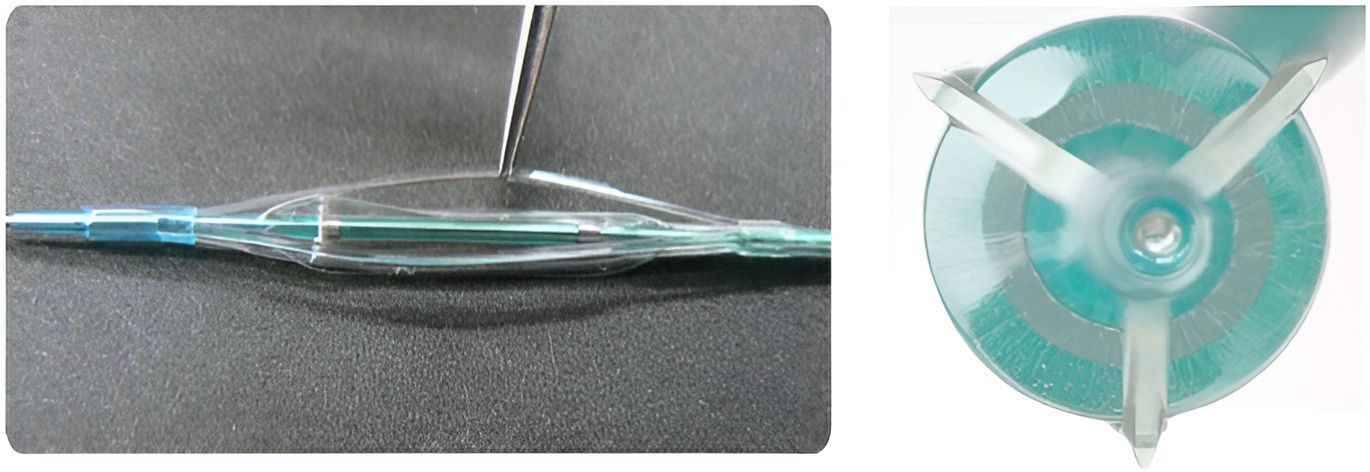

Compared to conventional balloons, cutting balloons offer the following advantages:
- The four microblades mounted on the balloon surface can cut through proliferative or calcified intima, effectively dilating hard stenoses in vessels.
- Compared to the blunt and uncontrolled expansion of conventional balloons, cutting balloons can achieve more balanced and complete dilation at lower pressures, resulting in minimal irregular tearing of the vessel intima, reduced vascular injury, milder inflammatory reactions, and a lower likelihood of vascular restenosis.
There are differences in expert consensus regarding the clinical application of scoring or cutting balloons in various peripheral vascular lesions. In some lesions, scoring or cutting balloons are used as adjunctive treatments (pre-treatment or lesion preparation), while in certain cases, they may serve as alternative treatment options.
1. Adjunctive Treatment (Pre-treatment or Lesion Preparation)
Renal Artery Stenosis
In 2017, the Chinese Society of Vascular Disease and Hypertension of the Chinese Medical Association released the "Chinese Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Renal Artery Stenosis." For patients with non-atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis (RAS) caused by large vessel vasculitis, the consensus pointed out that unsuccessful cases of PTA include immediate elastic recoil or dissection of the lesion after balloon dilation, and the lesion is too rigid to be adequately dilated, resulting in unsatisfactory imaging results. In such patients, selective stent placement or the addition of cutting balloon dilation may be one of the alternative treatment options. In this scenario, cutting balloons can be used as a pre-treatment option.
For patients with atherosclerotic RAS, the consensus suggests that interventional treatment methods include PTA and stent placement. The consensus recommends routine stent placement for atherosclerotic RAS to achieve satisfactory vascular reconstruction and reduce restenosis rates. However, for a small portion of lesions unsuitable for stent placement, balloon angioplasty may still be used. In this case, scoring or cutting balloons can serve as pre-dilatation devices before stent placement. In such scenarios, the use of scoring or cutting balloons reduces the hardness of the lesion site, decreasing the occurrence of recoil or dissection.
2. Lesion Treatment
Vascular Stenosis in Arteriovenous Fistulae
In 2019, the Vascular Access Working Group of the Chinese Hospital Association Blood Purification Center Branch released the "Chinese Expert Consensus on Vascular Access for Hemodialysis (2nd Edition)." Regarding the treatment of stenosis in autogenous arteriovenous fistulae, the consensus suggested the use of high-pressure balloon catheters, ultra-high-pressure balloon catheters, and special balloon catheters (such as guidewire-equipped balloon catheters, cutting balloon catheters, drug-eluting balloon catheters, and scoring balloon catheters). For the treatment of stenosis in arteriovenous fistulae, cutting balloon catheters and special balloon catheters with guidewires can be used as one of the clinical treatment methods.
Data presented at the 2022 Annual Academic Conference of the Chinese Medical Association Nephrology Physicians Branch showed that by the end of 2021, the number of registered hemodialysis patients in mainland China was nearly 750,000, with an average dialysis vintage of 50.9 months. With the continuous increase in the number of hemodialysis patients and the extension of dialysis vintage, the scientific maintenance of hemodialysis access becomes increasingly urgent. Currently, one of the pain points in clinical treatment is the relatively short postoperative patency time when using high-pressure balloon treatment.
In recent years, there have been continuous explorations and clinical studies internationally on the use of functional balloons (scoring, cutting) combined with drug-coated balloons (DCB) for PTA treatment of dialysis access. After treatment with scoring balloons, an excellent luminal gain rate can be achieved, providing adequate vascular preparation for DCB treatment, while the drug coating can penetrate the vascular intima, inhibit smooth muscle cell proliferation, and help achieve longer-lasting vascular patency.
1. DKutting, Dissolve™ AV by DK MedTech

Established in 2015, DK MedTech is a high-tech company specializing in the research and development, as well as production, of vascular interventional medical treatment products. Committed to continuous innovation and the pursuit of excellence and high-quality manufacturing, DK MedTech aims to address the complex current disease landscape. The company's business lines are primarily focused on coronary intervention, peripheral intervention, and neurointervention, providing corresponding solutions. DK MedTech has systematically developed over a dozen types of products and possesses independent PCT intellectual property rights.
(1) DKutting™
On November 21, 2022, DK MedTech's DKutting™ scoring balloon catheter received NMPA approval for marketing. DKutting™ high-pressure scoring balloon, the first domestically approved high-pressure directional expansion balloon for peripheral vessels, adopts exclusive patented design, combining excellent navigability and directional expansion capabilities. This product will bring a new choice for patients with peripheral vascular diseases and clinical surgeons.
DKutting™ high-pressure scoring balloon, independently developed by DK MedTech, adopts exclusive patented design, and has many advantages such as good navigability, uniform expansion, and high burst pressure. In terms of comprehensive product performance, this product can be called the "hexagonal warrior."

(2) Advantages of DKutting™
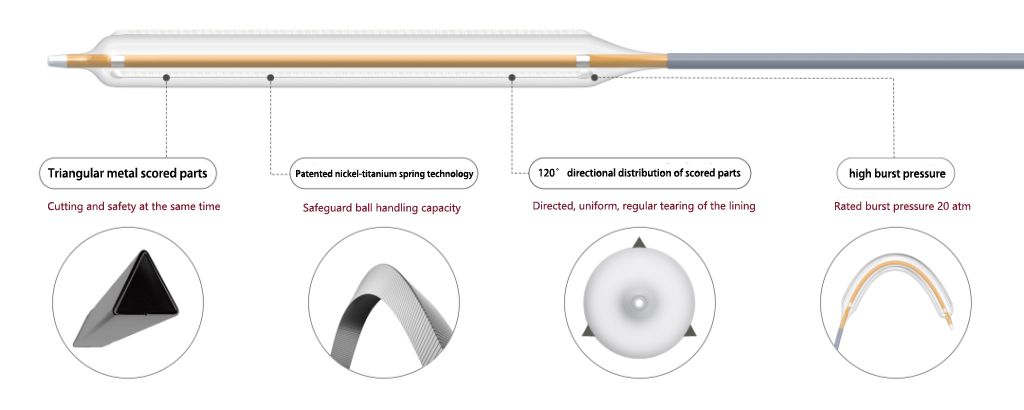
- DKutting™ high-pressure scoring balloon uses cutting parts made with the "triangular nitinol coil" technology, with an equilateral triangle cross-section. The three cutting parts are distributed at 120° angles and firmly fixed in the balloon working segment.
- For highly resistant narrow lesions, the cutting parts do not slide during expansion, and the triangular cross-section efficiently embeds into the vascular intima, assisted by a rated burst pressure of 20 atm, providing the necessary local high-pressure for directional expansion.
- For highly narrowed tortuous lesions, the No Base Bonding technology is used to further reduce the outer diameter of the balloon passage, while leveraging the advantages of radial flexibility of the coil design, significantly improving the balloon's navigability.
- DKutting™ high-pressure scoring balloon is compatible with 0.018"/0.035" guidewire systems, covering diameters from 4-8mm and lengths from 20-80mm. The push rod offers three options of 50/90/130cm, fully meeting the clinical needs of lower limb arteries and dialysis access.
(3) Dissolve™ AV
Dissolve AV, a scoring drug-coated balloon, is an innovative medical device specifically developed for patients with arteriovenous fistulas, making it the international first of its kind. This product combines three characteristics in one: cutting function + high burst pressure + drug coating.
Dissolve AV is a brand-new scoring drug-coated balloon that utilizes a cutting part made with a similar "triangular nitinol coil" technology as DKutting. Its cross-section is an equilateral triangle, with three cutting parts distributed at 120° angles, firmly fixed in the balloon working segment. For highly resistant narrow lesions, the cutting parts do not slide during expansion, and the triangular cross-section efficiently embeds into the vascular intima, assisted by a rated burst pressure of 20 atm, providing the necessary local high-pressure for directional expansion.
For highly narrowed tortuous lesions, the No Base Bonding technology is used to further reduce the outer diameter of the balloon passage, while leveraging the advantages of radial flexibility of the coil design, significantly improving the balloon's navigability.
The main difference between Dissolve AV and DKutting is that Dissolve AV's balloon working segment uniformly adheres to a paclitaxel coating with a concentration of 3µg/mm2.
Dissolve AV is compatible with 0.018"/0.035" guidewire systems, covering diameters of 4/5/6/7/8mm and lengths of 20/40/60/80mm. The push rod offers three options of 50/90/130cm.
RCT studies have been completed before market launch, and the clinical trial results fully reflect the following characteristics of this product:
- The world's first no-pre-dilatation DCB clinical trial: One-step operation, saving device usage.
- Combined cutting + high-pressure function: Higher expansion success rate compared to control group conventional PTA balloons.
- Uniform intimal tear: Patients experience lighter pain, reducing intimal injury.
- Paclitaxel coating: Inhibits excessive intimal hyperplasia, improving primary patency rate.
2. Becton, Dickinson and Company's UltraScore™, Vascutrak™

BD is a global medical technology company dedicated to advancing world health by improving medical discovery methods, medical diagnostic outcomes, and quality care. BD focuses on and supports frontline healthcare workers, striving to help patients improve clinical treatment and assist healthcare professionals in improving clinical workflows through the development of innovative technologies, services, and solutions.
(1) UltraScore™
UltraScore™ is suitable for dilating narrowings in peripheral vessels, as well as treating stenotic or obstructive lesions in autogenous or prosthetic vascular fistulas and recoating components of covered iliac artery stents, peripheral vascular balloon dilation stents, and self-expanding stents. This product is not intended for use in coronary arteries.
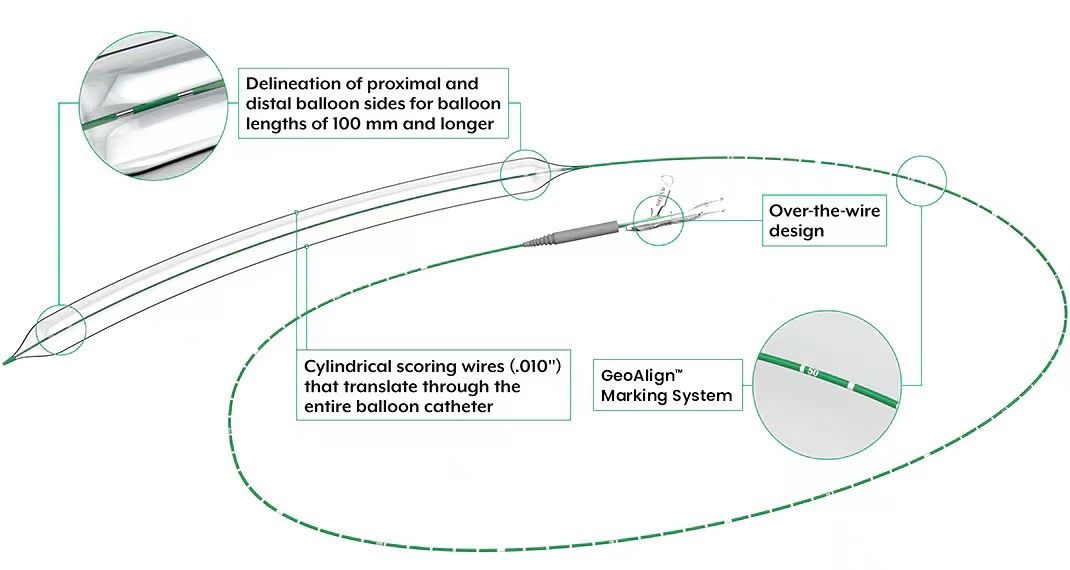
The UltraScore device is a semi-compliant balloon with two scoring wires spaced 180° apart, achieving focused pressure during dilation to optimize balloon expansion. Additionally, its opaque markers aid in positioning under fluoroscopy.
On March 5, 2024, Bard Peripheral Vascular officially released the UltraScore peripheral scoring balloon dilation catheter. As a dual-wire balloon, it has evolved with the concept of lumen preparation. Along with numerous subsequent functional balloons such as chocolate balloons, shockwave balloons, and others, it enriches clinical choices, ensuring that balloon dilation, as a fundamental technique, continues to thrive.
(2) VascuTrak™
VascuTrak dual-wire balloon entered the Chinese market in 2015. Its unique design, featuring integrated external wires and rapid wire exchange, enables focused expansion along the longitudinal axis on both sides of the vessel wall, ensuring low-pressure, safe, and orderly dilation. The emergence of peripheral dual-wire balloons addresses two major issues with traditional PTA balloon dilation. Firstly, insufficient expansion leading to elastic recoil and residual stenosis, and secondly, excessive expansion resulting in flow-limiting dissection formation.

The principle of the dual-wire balloon (VascuTrak) is to utilize the pressure focusing effect of nickel-titanium wires attached to the balloon surface, concentrating the expansion pressure on the external wires. Under the same pressure, a smaller contact area produces higher pressure, allowing for better expansion with relatively lower pressure. Additionally, VascuTrak offers lengths of up to 300mm, which, compared to shorter balloons, can also reduce dissection.
Due to its unique focused expansion effect, the dual-wire balloon has been primarily used in the treatment of recurrent stenosis in autogenous arteriovenous fistulas. Clinical evidence shows that besides improving the success rate of dilation, the dual-wire balloon significantly reduces patient pain and minimizes vascular injury.
3. Spectranetics Corporation's AngioSculpt
In 2017, Philips acquired the American minimally invasive surgical medical device manufacturer Spectranetics Corp to expand its leading position in the global image-guided therapy market and accelerate the expansion of image-guided therapy devices for treating cardiovascular and peripheral vascular diseases.

Spectranetics is an industry leader in vascular intervention for coronary and peripheral artery diseases, with its main products including devices for minimally invasive implantable cardiac pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs). The company's product portfolio also includes support catheters for promoting peripheral and coronary artery deblocking, as well as retrograde access and wire retrieval devices for treating peripheral artery obstructions, including chronic total occlusions.
The AngioSculpt XL PTA scoring balloon catheter is specifically designed to address common diffuse long-segment lesions in the lower extremity arteries. Currently available in lengths of 100 mm and 200 mm, it provides precise and effective 360° expansion. The scoring balloon technology of AngioSculpt offers a unique combination of controllable, effective dilation, and predictable device safety.
While the longer length of AngioSculpt XL provides greater coverage and convenience for lower extremity arterial procedures, it's the scoring technology of AngioSculpt that truly sets it apart.
(1) AngioSculpt Features
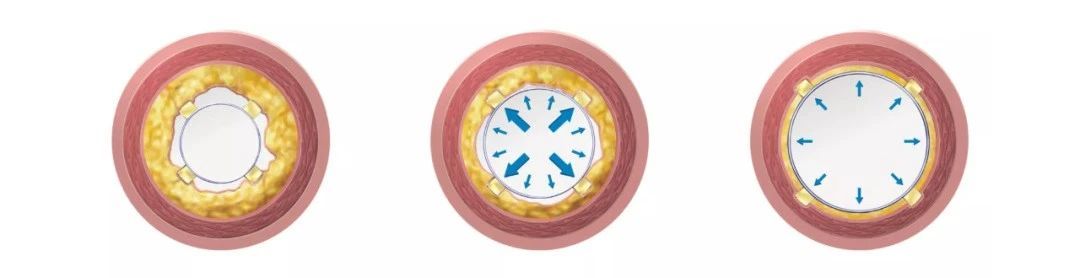
Precision
- Edge locking minimizes displacement.
- Rectangular scoring edges secure the device in place.
- Reduced risk of device slippage or "watermelon seed" effect, lowering the risk of damage to healthy tissue.
Dilation Force
- Approximately 15–25 times the scoring force.
- Designed to outwardly expand with about 15-25 times the driving force of traditional balloons.
- Spiral nitinol components of AngioSculpt ensure uniform initial lumen expansion.
Safety
- Outward expansion force designed for low dissection rates.
- Outward force from scoring equivalent to traditional balloons.
- Low dissection and minimal perforation rates.
- Low rates of adjunctive stent implantation and zero (0) flow-limiting dissection rates.
(2) Key Features of AngioSculpt XL
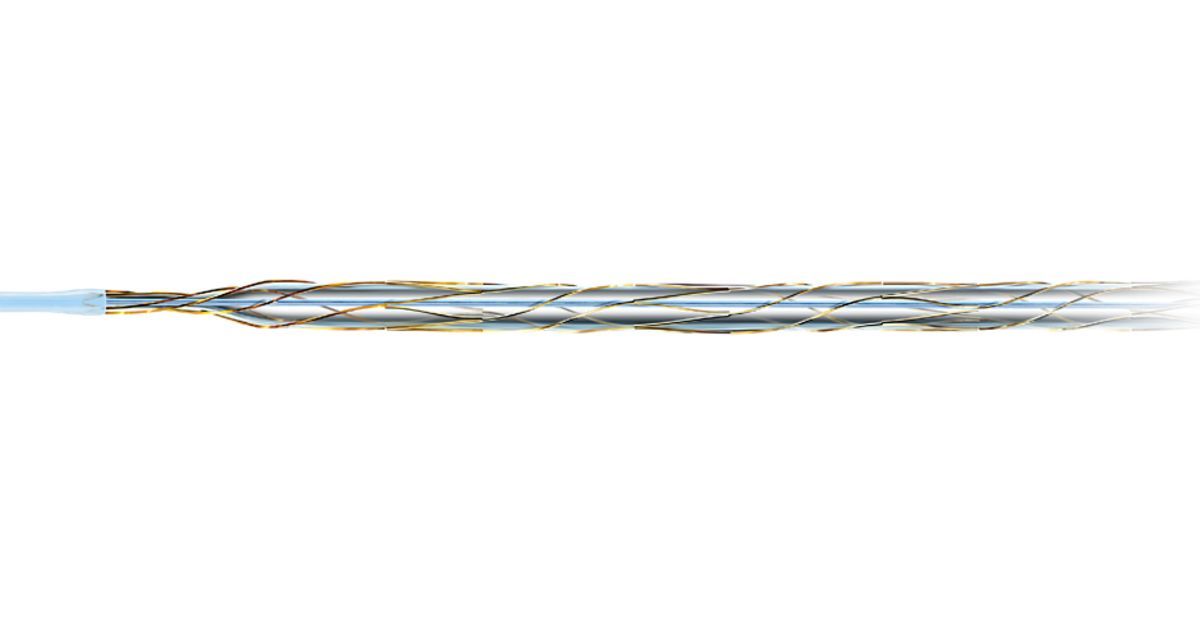
Nickel-titanium scoring elements arranged in a spiral structure for consistent scoring and safety, enabling predictable and precise operation—the only long balloon providing unique AngioSculpt benefits:
- Larger working pressure range (2–20 atm) allows customization of the device based on vessel size.
- Nickel-titanium reinforcement enables excellent balloon retraction and refolding capability.
- Electro-polished, helical scoring elements safely score lesions.
(3) Scoring Technology Highlights
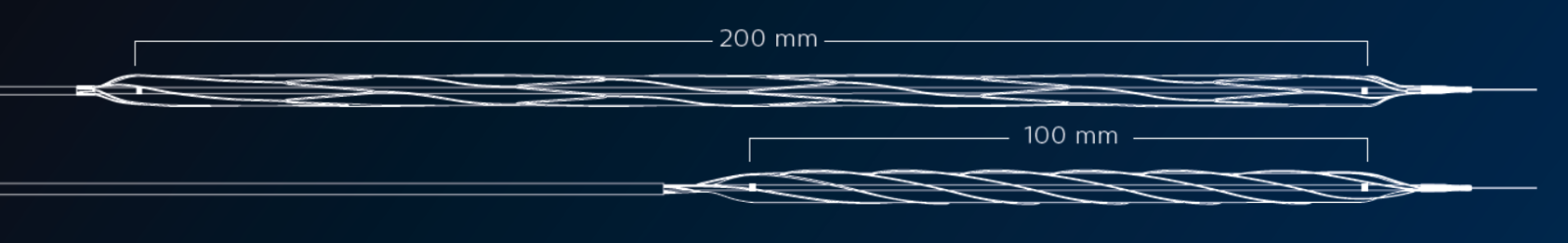
- Longer length size options and wider range of balloon diameters to meet the needs of diffuse long-segment lesions in lower limb vessels.
- Longer balloon length reduces inflation and shortens procedure time.
- Both 100 mm and 200 mm device specifications feature the unique AngioSculpt scoring technology.
- Offers a broader range of balloon size options.
4. BrosMed Medical's Tri-Wedge™
Founded in 2012, Guangdong BrosMed Medical Technology Co., Ltd. primarily focuses on the research and production of three categories of cardiovascular intervention medical devices, centered around balloons, catheters, guidewires, and accessories. Located in Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, serving as the provincial center for vascular intervention therapy and medical device engineering technology, BrosMed Medical has globally leading technologies in balloons and interventional catheters, along with a variety of globally exclusive products. Its products are sold in over 70 countries and regions worldwide, including China, the United States, Japan, Europe, the Middle East, and Latin America.

In October 2022, Tri-Wedge™, the triangular dragon peripheral vascular scoring balloon catheter, received market approval from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) after being on the market in Europe and South America for two years.
Developed by BrosMed Medical, the Tri-Wedge™ peripheral vascular scoring balloon catheter is suitable for dilating lesions in the tibial artery, femoral artery, popliteal artery, infrapopliteal artery, below-the-knee artery, and renal artery, and can be used to treat obstructive lesions in autogenous or artificial arteriovenous fistulae.
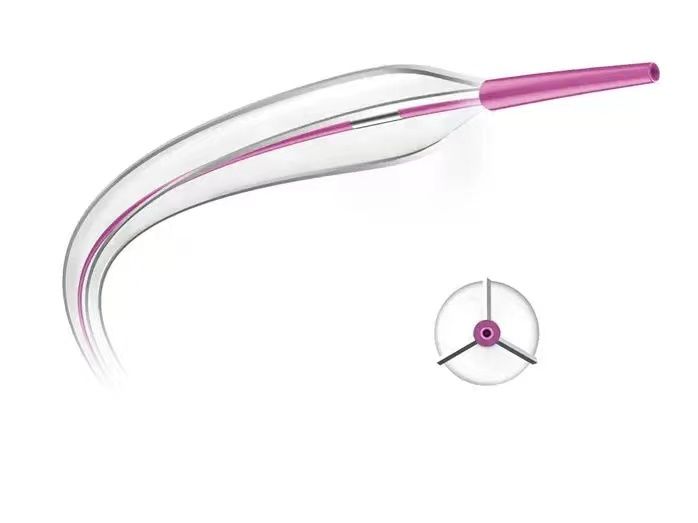
Tri-Wedge™ Product Features
Designed based on the principle of Focused Force, the scoring wires exert pressure on the vessel wall equivalent to ≥32 times the pressure of conventional high-pressure balloons. The balloon body is designed with high-pressure non-compliance, with a rated burst pressure of 20 ATM. With the combined action of the stress concentration of the scoring wires and the high-pressure balloon expansion force, it effectively opens up vascular calcification and intimal hyperplasia lesions.
Three triangular metal scoring wires are evenly distributed at intervals of 120° (patented fixation technology). As the balloon is progressively pressurized, the concentrated scoring wires embed into the vascular wall tissue, causing regular longitudinal tearing of the vascular intima, reducing the risk of uncontrolled tearing and dissection of the vessel wall under high pressure.

During the delivery process, the scoring wires are fully enveloped within the folded petals of the balloon, minimizing the outer diameter. The three metal wires traversing the entire balloon also enhance the pushability through tortuous and narrow lesions. The pre-tension and elastic design at both ends of the scoring wires ensure good conformity between the scoring wires and the balloon body during the expansion process.
5. ScoreFlexsPTA by Orbus Medical
In 1979, Mr. Qian Xuexiong founded Cordis Neich Medical in Hong Kong. Since Johnson & Johnson acquired Cordis in 1996, Neich Medical began developing its own line of balloon catheters. In the same year, Orbus Medical was established in the United States, focusing on cardiovascular stent development.

Scoreflex TRIO is the first domestically produced coronary three-wire scoring balloon catheter. The product is delivered through the radial or femoral artery pathway to the target lesion in the coronary artery along the guiding wire. With the two inherent wires attached to the balloon forming an external scoring component, the catheter generates localized high pressure on the luminal surface, allowing the balloon to open coronary artery lesions and dilate stenosis effectively at lower pressures. This process aids in reducing the risk of significant intimal tears and dissections, thereby improving blood flow and myocardial perfusion.
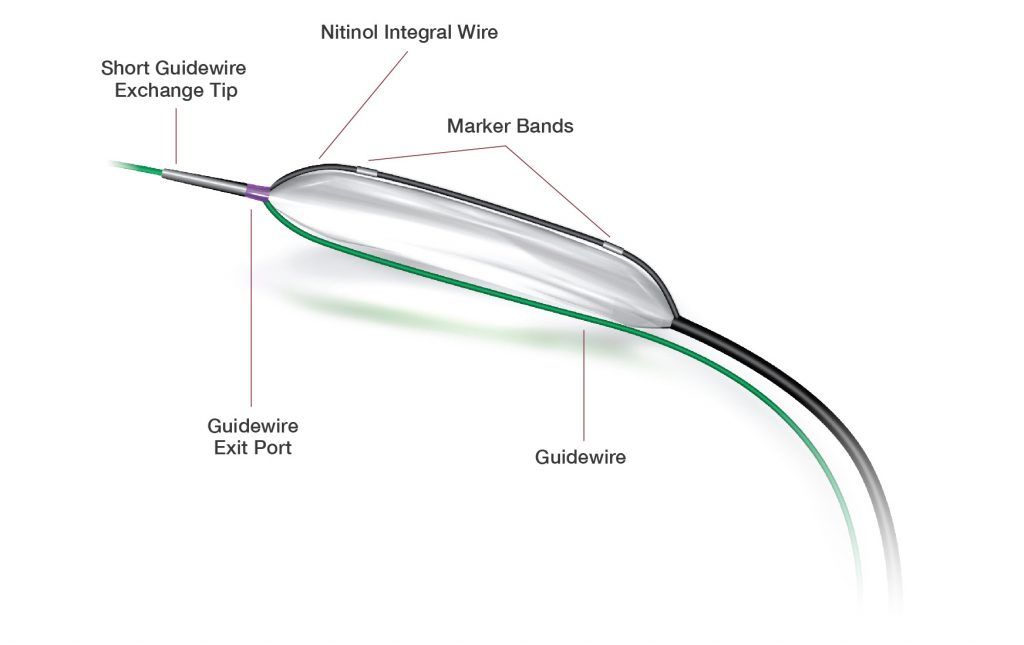
Scoreflex TRIO Features
Scoreflex TRIO features two metal wires on the outer surface of the balloon catheter, distributed at 180-degree intervals. The standard guiding wire assists the balloon in reaching the target lesion, while the wires fixed on the opposite side of the balloon aid in negotiating angled lesions. During balloon inflation, at lower pressures, the dual wires can engage plaque rupture, reducing the pressure exerted on the vessel wall and minimizing the elastic recoil of vascular lesions. The dual-wire design provides excellent pushability and strong capability to cross narrow lesions without displacement during dilation.
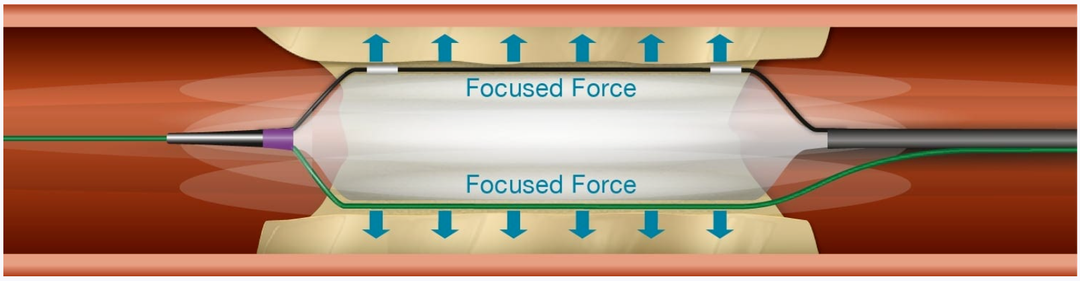
As a pre-dilatation balloon catheter used in PCI procedures, the longitudinally cutting expansion mode of Scoreflex TRIO, with its three wires, serves several purposes. Firstly, it further reduces residual stenosis compared to conventional balloon dilation, thus increasing procedural success rates. Secondly, it lowers the incidence of vascular intimal tears, reduces vascular injury, minimizes inflammatory reactions, enhances procedural safety, and decreases the occurrence of restenosis.